Romanticism Art Movement
Step into the captivating world of the Romanticism art movement, an extraordinary period that captivated the hearts and minds of artists and audiences alike throughout 19th-century Europe. Like a tempestuous tempest, Romanticism swept across the cultural landscape, challenging the rationality and restraint of the Enlightenment era. Instead, it embraced the tumultuous seas of emotions, individuality, and the awe-inspiring power of nature.
As we venture into the realms of Romanticism, we will uncover the artistic rebellion that sought to liberate the human spirit from the chains of convention. Unlike any other movement before it, Romanticism exalted the unrestricted expression of emotion, the boundless scope of imagination, and the profound connection with the natural world. Artists became poets, and their canvases transformed into lyric verses, breathing life into their innermost dreams, fears, and yearnings.
In this post, we will delve into the essence of Romanticism, its key characteristics, prominent artists, and the profound impact it had on the art world.
Exploring Romanticism Art Movement: A Journey into the Soulful Expressions of the 19th Century
What is the Romanticism Art Movement?
Romanticism was an artistic, literary, and intellectual movement that emerged in the late 18th and early 19th centuries as a profound reaction against the rationality, order, and scientific approach that characterized the Enlightenment period. Instead of embracing reason and the pursuit of objective truths, the Romantics celebrated the subjective experience, individuality, and the mysteries of the human psyche.
Recommended For You – 10 Romantic Paintings You Should Know
Key Themes and Characteristics of the Romanticism Art Movement
1- Embracing Emotion and Subjectivity
At the core of Romanticism lay a fervent embrace of emotions and subjectivity. Artists sought to convey the vast array of human sentiments, from the intense joy of love to the depths of sorrow and despair. They believed that emotions held the key to understanding the human experience and, through their art, aimed to evoke a visceral response from the viewer.

The Lady of Shalott, 1888 by John William Waterhouse – Romanticism Art Movement.
2- The Sublime and Nature’s Grandeur
A central theme of Romanticism was the notion of the sublime – the overwhelming experience of awe and terror in the face of nature’s grandeur and vastness.
Artists often depicted awe-inspiring landscapes, dramatic seascapes, and majestic mountain ranges, portraying nature as a powerful and untamed force. Through these scenes, they sought to evoke a sense of the divine and the transcendent, leaving the viewer humbled by the sheer magnitude of the natural world.
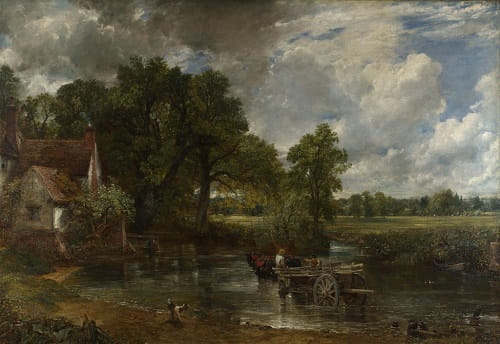
The Hay Wain, 1821 by John Constable – Romanticism Art Movement.
Recommended For You – 10 Places From Famous Paintings That You Can Visit in Real Life
3- Escapism and the Exotic
Romantic artists often turned to distant lands and exotic cultures for inspiration. They found allure in the unknown and the mysterious, imagining far-off places filled with adventure and danger. This fascination with the exotic allowed them to break free from the constraints of their own reality and explore realms of imagination and fantasy.

The Sea of Ice, 1823-1824 by Caspar David Friedrich – Romanticism Art Movement.
4- Love for the Medieval and Gothic
The Romantic period also saw a revival of interest in medieval and Gothic themes.
Artists were drawn to the medieval era’s chivalry, heroism, and sense of honor, as well as the mysterious and sometimes eerie atmosphere of Gothic architecture and literature. This nostalgia for the past and a longing for a simpler, more authentic world were significant aspects of the Romantic sensibility.
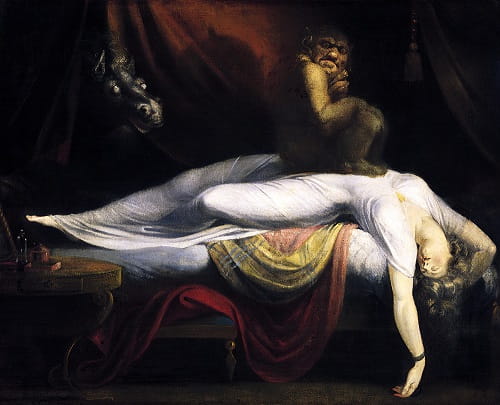

The Nightmare, 1781 – Henry Fuseli – Romanticism Art Movement.
5- Political and Social Commentary
In addition to exploring emotions and the natural world, Romantic artists often used their works to comment on contemporary political and social issues. They critiqued the Industrial Revolution, social inequality, and the consequences of rapid urbanization, expressing empathy for the plight of the downtrodden and marginalized.

The Raft of the Medusa, 1819 by Theodore Gericault – Romanticism Art.
Recommended For You – The Raft of the Medusa Analysis: A Masterpiece of Romanticism and Tragedy
6- The Imagination as a Source of Creativity
For Romantics, the imagination was a wellspring of creativity. They believed that art should be a product of the artist’s inner visions, dreams, and subconscious mind. This emphasis on the imagination allowed for a vast range of artistic styles and expressions, from dreamlike and fantastical to deeply emotional and introspective.
7- Symbolism and Allegory
Symbolism and allegory played a significant role in Romantic art, with artists using visual metaphors to convey deeper meanings and profound messages. Everyday objects, natural elements, and even colors were laden with symbolic significance, inviting viewers to engage in an interpretative journey through the artwork.

The Death of Sardanapalus, 1827 by Eugene Delacroix – Romanticism Art.
Famous Romantic Painters and Their Masterpieces
1- Caspar David Friedrich (1774-1840)
Caspar David Friedrich, a German painter, is renowned for his hauntingly evocative landscapes and profound exploration of the human experience in nature.
One of his most famous works is “Wanderer above the Sea of Fog” (1818). In this masterpiece, a lone figure stands atop a rocky precipice, gazing into the misty expanse of a rugged landscape, symbolizing the human quest for understanding and connection with the sublime.

Wanderer above the Sea of Fog, 1818 by Caspar David Friedrich – Romanticism Art Movement.
Recommended For You – Wanderer above the Sea of Fog: An In-Depth Analysis of Caspar David Friedrich’s Masterpiece
2- Joseph Mallord William (J.M.W.) Turner (1775-1851)
Joseph Mallord William Turner, a British artist, was a master of capturing the interplay of light and atmosphere in his landscapes. His painting “The Slave Ship” (1840) is a powerful and emotionally charged work that depicts a ship in a storm, with enslaved Africans thrown overboard.

The Slave Ship, 1840 by Joseph Mallord William (J.M.W.) Turner – Romanticism Art.
Recommended For You – Turner’s “The Slave Ship” Analysis
The vivid portrayal of turbulent seas and the horrors of the transatlantic slave trade served as a poignant social commentary on the injustices of the time.
3- Francisco Goya (1746-1828)
Spanish painter and printmaker Francisco Goya’s works delved into the darker aspects of human nature, reflecting the tumultuous political and social climate of his era.
One of his iconic pieces is “The Third of May 1808” (1814), portraying the brutal execution of Spanish civilians by French soldiers during the Peninsular War.

The Third of May 1808, 1814 by Francisco Goya – Romanticism Art Movement.
Recommended For You – The Third of May 1808: Decoding Goya’s Masterpiece of Courage and Tragedy
Goya’s use of light and shadow, coupled with intense emotion, makes this artwork a haunting depiction of the horrors of war.
4- Eugène Delacroix (1798-1863)
Eugène Delacroix, a French painter, is celebrated for his use of vibrant colors and dramatic compositions. His painting “Liberty Leading the People” (1830) has become an enduring symbol of the July Revolution in France.
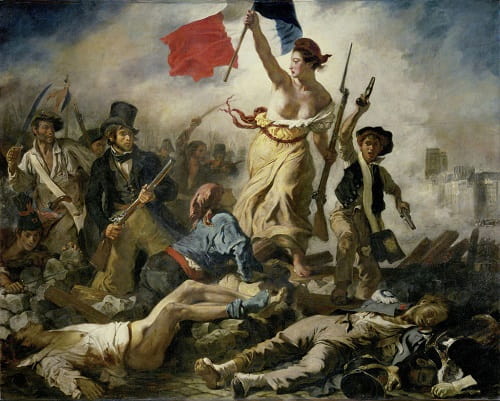

Liberty Leading the People, 1830 by Eugène Delacroix – Romanticism Art Movement.
The artwork features a female allegorical figure of Liberty leading a diverse group of revolutionaries, representing the fight for freedom and the triumph of the people.
Recommended For You – The Influential Women of Art History
5- William Blake (1757-1827)
English poet, painter, and printmaker William Blake was a visionary artist who merged poetry and visual art in a unique and mystical style. His series of illuminated books, such as “Songs of Innocence and of Experience” (1789-1794), exemplified his exploration of themes related to innocence, experience, and the complexities of the human soul.

Songs of Innocence and of Experience, 1789-1794 by William Blake – Romanticism Art.
6- John Constable (1776-1837)
John Constable, an English landscape painter, is celebrated for his idyllic depictions of the English countryside. His masterpiece “The Hay Wain” (1821) is an iconic representation of rural life, with a horse-drawn cart crossing a river amid a picturesque landscape.
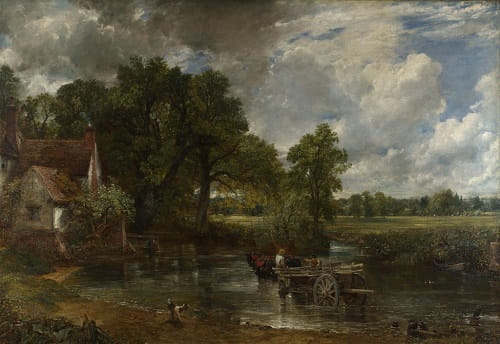
The Hay Wain, 1821 by John Constable – Romanticism Art.
Constable’s meticulous attention to detail and love for nature captured the essence of the Romantic appreciation for the beauty of the natural world.
Romanticism Movement
In conclusion, the Romanticism art movement stands as a testament to the enduring power of human emotion, individuality, and the awe-inspiring beauty of nature. Throughout the 19th century, this revolutionary period in art history challenged the rationality of the Enlightenment era, embracing the boundless realms of imagination and the complexities of the human soul.
Romanticism‘s impact on the art world remains palpable, as contemporary artists draw from its rich legacy to create works that resonate with audiences on a profound level. The movement’s celebration of individual expression continues to inspire artists to fearlessly explore their innermost thoughts, feelings, and experiences through their chosen medium.

The Kiss, 1859 by Francesco Hayez – Romanticism Art Movement.
Moreover, the Romantic reverence for nature’s grandeur and the sublime continues to influence artists who seek to convey the majestic beauty of the natural world, while also drawing attention to environmental issues and the urgent need for conservation.
The Romantic tradition of using art as a vehicle for social and political commentary remains relevant today, with artists leveraging their creative prowess to shed light on pressing global challenges and advocate for positive change. Through thought-provoking and emotionally charged works, they call on society to reflect on its values and responsibilities.
Furthermore, the Romantic ideals of imagination and fantasy find expression in various forms of artistic creation, from literature to film and beyond. By embracing the fantastical and the surreal, artists continue to push the boundaries of human imagination, transporting audiences to captivating realms of wonder and introspection.
The Romanticism art movement‘s lasting influence serves as a reminder of the enduring power of art to touch the depths of the human soul and connect us to the beauty and mysteries of the world. As we continue to cherish and learn from the masterpieces of Romantic artists, their legacy propels us to embrace the richness of our emotions, appreciate the sublime in nature, and use our creative endeavors to advocate for a better and more empathetic world.
References:
- https://www.expedia.co.uk/stories/the-10-best-paintings-in-romanticism/
- https://tr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Romantizm
- https://www.khanacademy.org/humanities/becoming-modern/romanticism/romanticism-in-england/a/henry-fuseli-the-nightmare
- https://www.portraitflip.com/blog/paintings-of-romanticism/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Slave_Ship
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Third_of_May_1808








